Nowadays, we can see that many plants need to use plant growth lights, and in some new plant experiments, plant lights are also used. What is the principle of plant light? Why do so many plants need plant lights? Today, let’s talk about the principle of plant growth lights.
The principle of plant grow lights
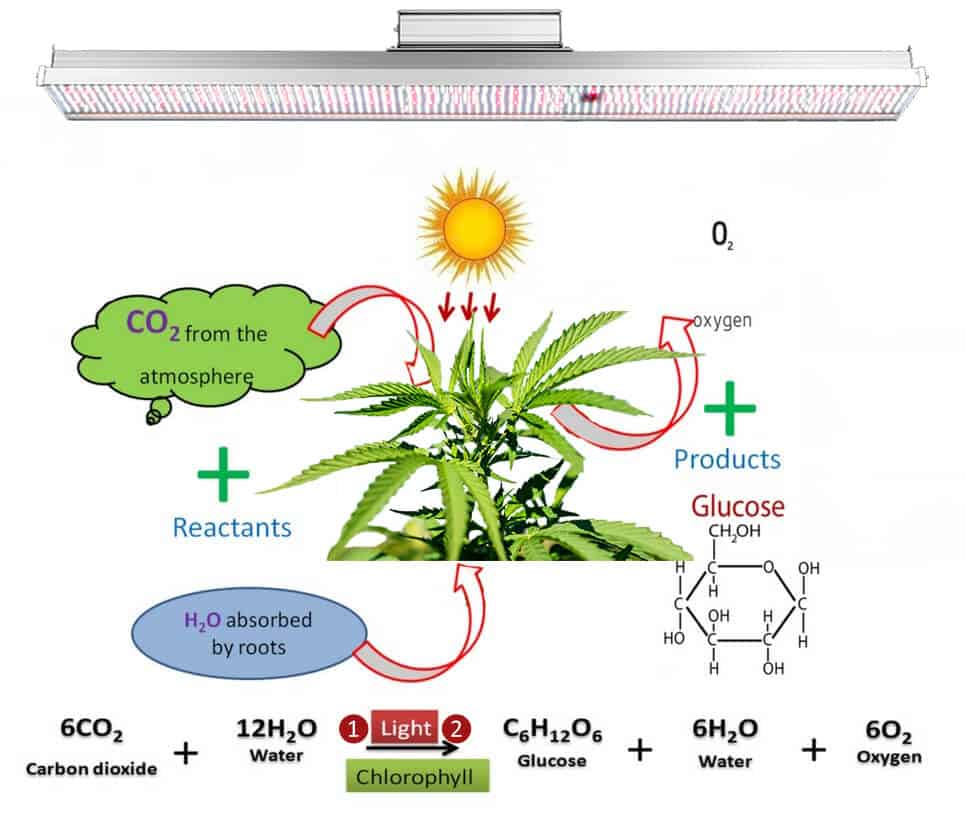
Efficiently convert electrical energy into radiant energy. Achieving high radiation intensity in the effective range of photosynthesis, especially low infrared radiation (thermal radiation) The emission spectrum of the bulb meets the physiological requirements of plants, especially in the effective spectral region of photosynthesis.
Grow lights are artificial light sources, usually electric, designed to stimulate plant growth by emitting an electromagnetic spectrum suitable for photosynthesis. Grow lights are used in applications that do not have natural lighting or require supplemental lighting. Artificial lighting is a must on cloudy and low-intensity days. Give crops at least 8 hours of light per day at night, and the time of day should be fixed. But lack of nighttime rest can also lead to disordered plant growth and reduced yields. Under the fixed environmental conditions such as carbon dioxide, water, nutrients, temperature and humidity, the size of the “photosynthetic light flux density PPFD” between the light saturation point and the light compensation point of a specific plant directly determines the relative growth rate of the plant. Therefore, an efficient light source PPFD Combination is the key to plant planting efficiency.
Why do so many plants need plant lights?
1. Plant lights are needed for planting in winter. Because there is less light in winter, plant lights need to be used for supplementary light.
2. Indoor planting environments, such as planting succulent or other ornamental plants, need to use plant lights to adjust the spectrum and make plants grow beautifully.
3. When planting off-season plants or other plants in greenhouses, both the light intensity and light time affect the growth of crops. If the light intensity is lower than the compensation point of the crop, the organic matter produced by photosynthesis will not be able to keep up with the speed of consumption. , which will affect the growth of plants and cause serious death. In low light conditions, the plants will also appear leggy and weak. Under the influence of cloudy and hazy weather, the illumination is even more insufficient, and the photosynthetic rate will drop sharply, and it will also cause pests and diseases, causing serious losses.
